وبلاگ
7 4 Basic EPS
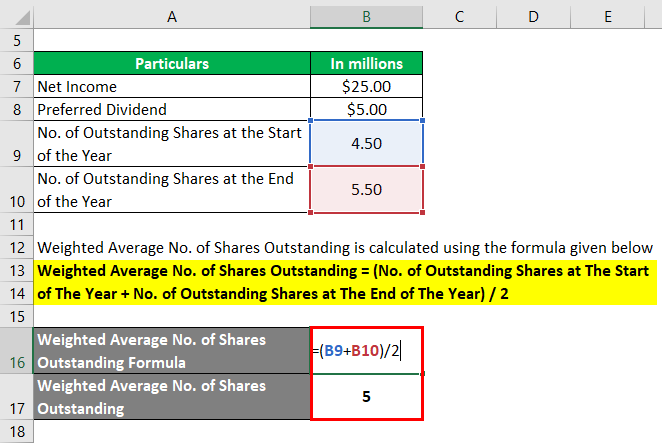
WASO’s primary application is in calculating EPS, a key indicator of a company’s profitability on a per-share basis. It’s crucial for investors who utilize EPS to compare companies’ financial health. An increasing WASO might dilute EPS, potentially affecting investor perceptions and company valuations. In calculating WASO, the period each share batch has been outstanding within a reporting period is accounted for, giving a temporally adjusted average that more accurately reflects the company’s share structure.
What is the Weighted Average of Outstanding Shares? How is It Calculated?
Along with individual shareholders, this includes restricted shares that are held by a company’s officers and institutional investors. The weighted average of shares outstanding is calculated based on the volumes of various share sales and purchases over a period of time. The weighted average calculation incorporates the beginning number of shares outstanding, plus additional shares that were sold or otherwise issued during the period, minus any shares that were bought back during the period. The weighted average number of shares is determined by taking the number of outstanding shares and multiplying it by the percentage of the reporting period for which that number applies for each period. In other words, the formula takes the number of shares outstanding during each month weighted by the number of months that those shares were outstanding.
AccountingTools
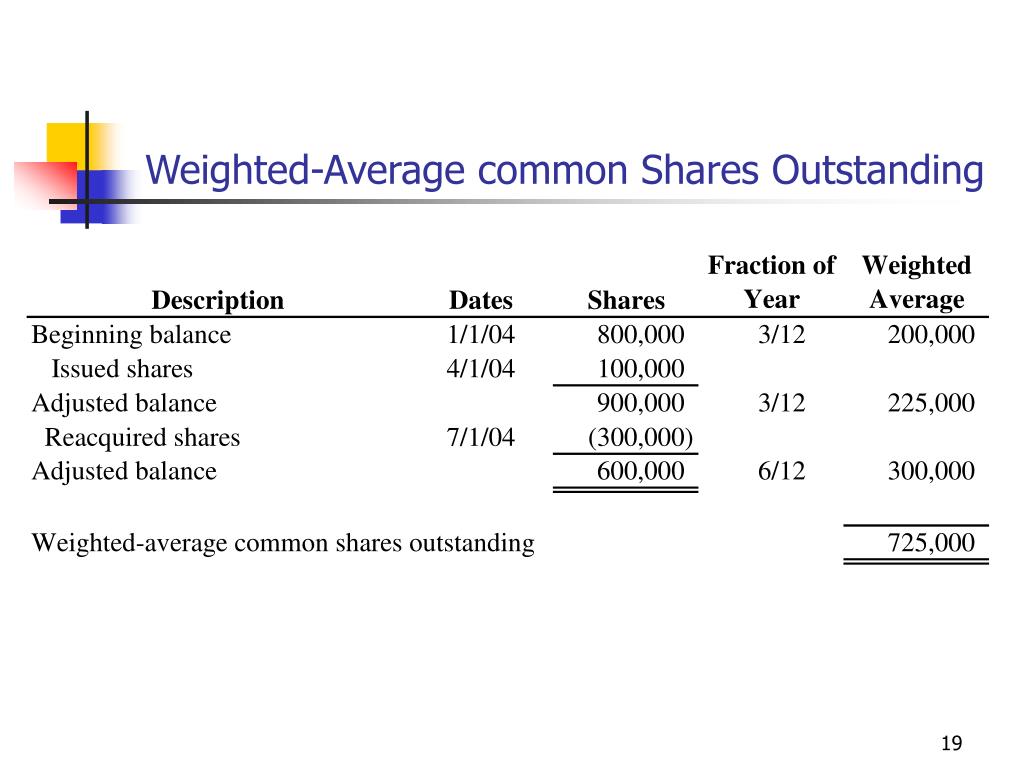
Group 2 consists of the 8,000 shares outstanding from 1 April to the end of the year and group 3 is the 12,000 shares outstanding from 1 April to 31 August. The weighting of each group by the fraction of the year it was outstanding is shown below. Below is the Weighted Average Shares calculation example when shares are issued and repurchased during the year.
Steps to Calculate Weighted Average Shares Outstanding
However, the value of each individual share is inversely related to the number of shares outstanding. This relationship makes understanding the dynamics of shares outstanding crucial for investors and industry analysts. In this case, the same result could have been achieved by multiplying the 111,000 shares from Example 1 by a factor of 2.
What are some examples of weighted average shares outstanding calculations?
- “Shares outstanding” also is a line in the data that is displayed with any stock quote.
- In above example, notice that Maria Company has adjusted all shares that exist prior to stock dividend (i.e., from January 1 to June 1).
- Of the 40,000 split shares issued on 1 April, group 2 consists of 16,000 considered to have been outstanding from 1 April to 31 December, and group 3 is composed of 24,000 that were outstanding from 1 April to 31 August.
- The weighted average number of outstanding shares in our example would be 150,000 shares.
- Due to these factors, the actual number of shares outstanding can vary over the course of a reporting period.
- We pro-rated the weighted average number of shares according to their duration.
For example, if the denominator includes the whole of a group of new shares issued late in the year, it would not be consistent with the earnings derived from the resources available to the firm throughout the entire year. The below table shows the weighted averages shares outstanding calculation in a tabular format. Treasury stock consists of shares that the company has acquired in a buyback. These shares are held in the corporation’s “treasury” rather than in circulation and are therefore excluded from the number of outstanding shares.
Shares outstanding refers to the amount of stock held by shareholders, including restrictive shares held by company insiders. A company, however, may have authorized more shares than the number of outstanding but has not yet issued them. These may later appear in the form of a secondary offering, through converting convertible securities, or issued as part of employee compensation such as stock options. Due to these factors, the actual number of shares outstanding can vary over the course of a reporting period.
For example, the opening figure of 500,000 remained unchanged for 3 months (i.e., 25% of the total time of the year) until the start of the second quarter, after which it changed. Notice that Alpha Inc. has ignored 25,000 shares issued on December 31 in above computation. The reason is that what are different types of standards under standard costing these shares have been issued on the last day of the year and have not been outstanding during the year 2022. Changes occur due to stock issuance, buybacks, or corporate actions like splits. Each affects the share count differently but must be accurately reflected in financial analysis.
Given continuously changing stock prices, the investor will calculate a weighted average of the share price paid for the shares. To calculate the weighted average cost per share, the investor can multiply the number of shares acquired at each price by that price, add those values, and then divide the total value by the total number of shares. Shares outstanding are the stock that is held by a company’s shareholders on the open market.
This journey through the nuances of WASO not only clarifies its importance but also empowers investors and analysts to make informed decisions. Ask a question about your financial situation providing as much detail as possible. We follow strict ethical journalism practices, which includes presenting unbiased information and citing reliable, attributed resources. Finance Strategists is a leading financial education organization that connects people with financial professionals, priding itself on providing accurate and reliable financial information to millions of readers each year. At Finance Strategists, we partner with financial experts to ensure the accuracy of our financial content.
These include a company’s market capitalization, such as market capitalization, earnings per share (EPS), and cash flow per share (CFPS). Weighted average shares outstanding is the number of company shares after incorporating changes in the shares during the year. E.g., buyback of shares, the new issue of shares, share dividend, stock split, conversion of warrants, etc. Thus, while calculating Earnings per Share, the Company needs to find the weighted average number of shares outstanding. It incorporates all such scenarios of changes in the weighted average number of shares to give fair Earnings per share value. Typically, a stock split occurs when a company is aiming to reduce the price of its shares.